Slope of the v vs. t Graph, Acceleration
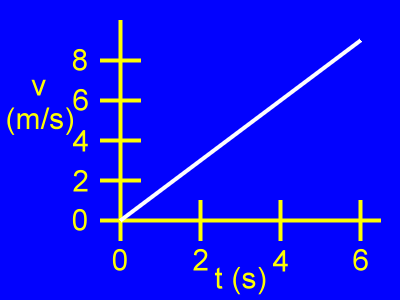
Here is a v vs. t, or velocity vs. time, graph.
Velocity (v) is vertical.
Time (t) is horizontal.
Initially, when t = 0 s, the velocity of the object is v = 0 m/s.
From then on as time passes the object moves with a greater and greater positive velocity.
Let's look at two points on this graph....
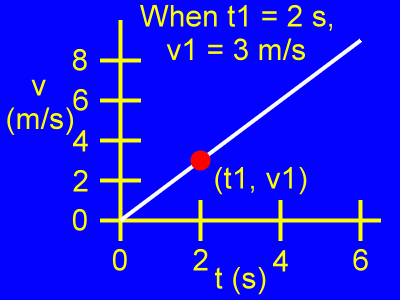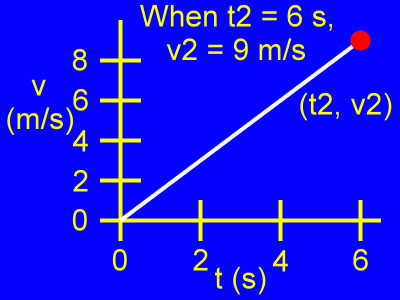
Examine the first point, (t1, v1).
When t1 = 2 s, then v1 = 3 m/s.
Examine the second point, (t2, v2).
When t2 = 6 s, then v2 = 9 m/s.
Let's find the slope of this graph using those two
points...
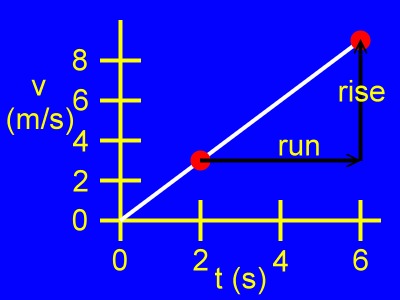
Using those two points, here is the rise and the
run of the slope of this
v vs. t graph.
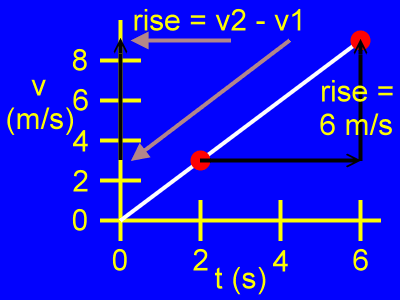
Here, the rise is the difference of the velocity coordinates, or v2 - v1, as in:
rise = v2 - v1
rise = 9 m/s - 3 m/s
rise = 6 m/s
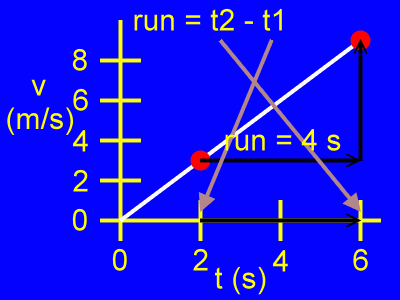
Here, the run is the difference of the time coordinates, or t2 - t1, as in:
run = t2 - t1
run = 6 s - 2 s
rise = 4 s
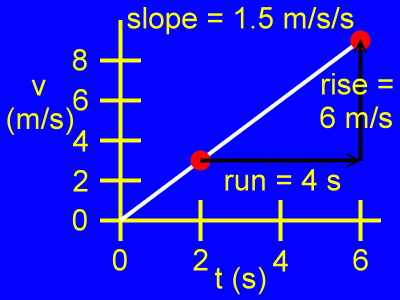
The slope of this graph is a change in velocity divided by a change in time, as in:
slope = rise / run
slope = 6 m/s / 4 s
slope = 1.5 m/s/s (or m/s2)
This slope is the acceleration of the object, since acceleration is defined as the change in velocity divided by the change in time.
So, acceleration = 1.5 m/s/s.